Dilated Cardiomyopathy Is A Disorder That Leads To The Heart Muscle To Weaken And Enlarge
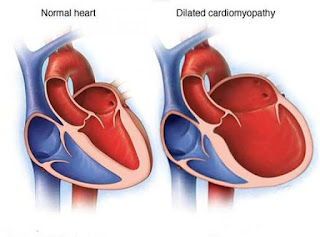 |
| Dilated Cardiomyopathy |
Cardiomyopathy is classified into several types. Dilated Cardiomyopathy is the most common type, but it can be caused by a variety of underlying conditions. Some doctors use the term to refer to a particular condition known as idiopathic Dilated Cardiomyopathy. As a result, the heart is unable to pump enough blood to the rest of the body. There isn't a known cause of this type of Dilated Cardiomyopathy. Heart valve problems, arrhythmia and blood clots in the heart, heart failure, and even sudden cardiac death can all result from Dilated Cardiomyopathy. Damage to the heart muscle from certain diseases, such as hemochromatosis, is a risk factor for Dilated Cardiomyopathy. There is a history of Dilated Cardiomyopathy, heart failure, or sudden cardiac arrest in the family. Valve disease of the heart
Heart disease caused by a narrowing or blockage in the
coronary arteries is the most common cause of Dilated Cardiomyopathy. High blood
pressure that is not well controlled. Alcohol or cocaine (or other illegal drugs) abuse is one of many other causes of Dilated Cardiomyopathy. Diabetes,
thyroid disease, or hepatitis are all possibilities. Medicines that can be
harmful to the heart, such as cancer treatments. Abnormal heart rhythms occur
when the heart beats very quickly for an extended period of time. Autoimmune
diseases, Diseases that run in families,
Infections involving the heart muscle, Heart valves that are too narrow or
leaky, During the final month of pregnancy or within five months of the baby's
birth, Exposure to heavy metals such as lead, arsenic, mercury, and cadmium.
It is critical
to identify people who are at high risk of cardiomyopathy. After all, some
people with cardiomyopathy have no symptoms at all. Others have no signs or
symptoms of the disease in the early stages. People without symptoms who
recognize their increased risk for cardiomyopathy have a better chance of being
diagnosed early, when treatment may be most effective. Cardiomyopathy symptoms
and signs include: Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing, particularly during
physical exertion, Fatigue, Swelling in the ankles, feet, legs, abdomen, and
neck veins, Dizziness , Light-headedness , Fainting while participating in
physical activity , Arrhythmias (abnormal heartbeats) (abnormal heartbeats)Chest
pain, particularly after physical exertion or large meals, Murmurs in the
heart (unusual sounds associated with heartbeats).
Complications of Dilated
Cardiomyopathy include Heart
failure: The heart cannot pump enough blood to meet the body's needs, and Heart
failure can be fatal if left untreated. Heart valve leakage (heart valve
regurgitation): Cardiomyopathy can make it difficult for heart valves to close,
Blood may leak backward through a heart valve. Irregular heartbeats
(arrhythmias): Changes in the heart's size and shape can disrupt its rhythm. Sudden
cardiac arrest: Dilated Cardiomyopathy can cause the heart to stop beating
abruptly. Blood clots: Blood clots can form as a result of blood pooling in the
left lower heart chamber. Clots in the bloodstream can obstruct blood flow to
other organs, including the heart and brain, Blood clots can cause a stroke, a
heart attack, or damage to other organs, Arrhythmias may also occur in clots in
the blood. Healthy lifestyle habits can aid in the prevention or reduction of Dilated
Cardiomyopathy complications. There are
some heart-healthy approaches: Avoid or limit the consumption of alcohol, and smoking is prohibited. Don't experiment with cocaine or other illegal drugs.
Consume a healthy- low-sodium diet (sodium). Receive adequate rest and sleep.
Get some exercise on a regular basis. Keep a healthy weight. Control your
stress. Dilated Cardiomyopathy can
be reversed in some cases. Treatment may improve symptoms. Other types of Dilated
Cardiomyopathy are irreversible, with long-term damage. Although there is no
cure for Dilated Cardiomyopathy, most of the symptoms can be managed with
medication and other treatments to allow you to lead an ordinary life. The type
of medication or treatment required will be determined by the symptoms.
Comments
Post a Comment