During Atrial Fibrillation, The Top Chambers Of The Heart Beat Chaotically And Irregularly, Goes Out Of Rhythm With The Bottom Chambers
 |
| Atrial Fibrillation Market |
Atrial Fibrillation (A-fib) is an arrhythmia (an irregular and typically very fast heart rhythm) that can result in blood clots in the heart. Stroke, heart failure, and other heart-related problems are all worsened by Atrial Fibrillation. (the ventricles). Many patients with A-fib have no symptoms. A-fib, on the other hand, can induce a rapid, hammering heartbeat (palpitations), shortness of breath, or weakness. Atrial Fibrillation episodes can be intermittent or continuous.
Although A-fib is seldom fatal, it is a significant medical
disease that requires prompt treatment to avoid stroke. Medication, treatment
to reset the heart rhythm, and catheter procedures to block defective cardiac
impulses may all be used to treat Atrial Fibrillation. A person who has Atrial Fibrillation may also have an atrial flutter, which is a similar heart rhythm
disorder. Although atrial flutter is a distinct arrhythmia, therapy is quite
similar to that of Atrial Fibrillation.
Some persons with Atrial Fibrillation (A-fib) are
asymptomatic. Individuals who have Atrial
Fibrillation symptoms may have the following signs and symptoms:
Palpitations (fast, fluttering, or hammering heartbeat), Chest discomfort,
Dizziness, Fatigue, Light-headedness, Decreased ability to exercise, Shortness
of breath, and Weakness. Understanding the causes of A-fib may be aided by
understanding how the heart normally beats.
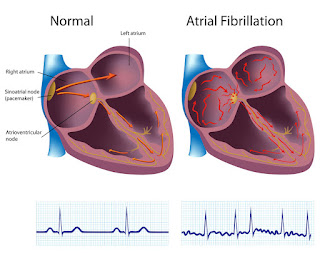
The normal heart contains four chambers: two upper (atria)
and two lower (ventricles) (ventricles). The sinus node is a collection of
cells located in the upper right chamber of the heart (right atrium). The sinus
node is the natural pacemaker of the heart. It generates the signal that
initiates each heartbeat. The signal from the sinus node goes through the two
upper heart chambers in a regular cardiac beat (atria), The signal travels
through the atrioventricular (AV) node, which connects the upper and lower
chambers. When the signal moves, the heart squeezes (contracts), sending blood
to the heart and body.
Comments
Post a Comment